The financial sector is the backbone of any modern economy, and its stability relies heavily on the ability to withstand and recover from operational disruptions. The Saudi Central Bank (SAMA), formerly the Saudi Arabian Monetary Authority, has long been at the forefront of introducing regulatory standards to safeguard the Kingdom’s financial ecosystem.
SAMA CRFR Saudi Arabia Complete Guide to the Cyber Resilience Framework
In its continuous effort to strengthen resilience against operational and cyber-related threats, SAMA introduced the Cyber Resilience Framework for Regulated Entities (CRFR). This framework outlines a structured approach for financial institutions to anticipate, withstand, respond to, and recover from disruptions — whether caused by cyberattacks, technology failures, or other operational incidents. The CRFR is not merely about compliance — it’s about embedding resilience into the DNA of financial organizations, ensuring uninterrupted critical services to customers and the wider economy. Read more: SAMA CSF | SAMA MVC
Understanding the SAMA CRFR
The CRFR is designed specifically for SAMA-regulated entities, which include:
- Banks
- Insurance companies
- Financing companies
- Payment service providers
- Other licensed financial institutions
It aims to ensure that all these entities can:
- Identify critical services they provide.
- Assess vulnerabilities and potential impacts.
- Establish robust defense and recovery measures.
- Maintain public confidence even during severe disruptions.
The CRFR draws inspiration from international resilience standards such as:
- BCBS (Basel Committee on Banking Supervision) Principles for Operational Resilience.
- NIST SP 800-34 for contingency planning.
- FSSCC Cybersecurity Profile for financial services.
Why SAMA Introduced the CRFR
Several key factors drove the creation of the CRFR:
- Evolving Threat Landscape
Cyber attacks are becoming more sophisticated, targeting not just data but also operational capabilities. - Digital Transformation Risks
As Saudi Arabia’s Vision 2030 pushes for digitization in banking and finance, the potential for system disruptions increases. - Interconnected Financial Ecosystem
A disruption at one financial institution can cause ripple effects across the sector. - Customer Trust & Economic Stability
Financial resilience ensures customer trust, which is vital for economic stability.
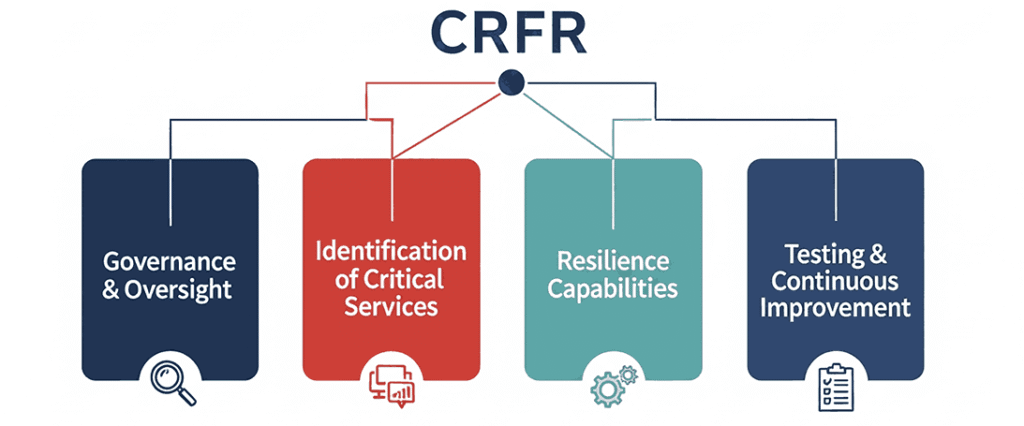
Structure of the CRFR
The CRFR is built around four core pillars, each containing several requirements:
| Pillar | Purpose | Example Requirements |
|---|---|---|
| Governance & Oversight | Establishing leadership responsibility and clear roles for resilience. | Board oversight, resilience strategy approval. |
| Identification of Critical Services | Understanding and mapping essential business functions. | Service dependency mapping, criticality ranking. |
| Resilience Capabilities | Implementing the ability to withstand and recover from disruptions. | Redundancy systems, incident response teams. |
| Testing & Continuous Improvement | Regularly validating and enhancing resilience measures. | Scenario-based testing, lessons learned reviews. |
Implementation Process for the CRFR
Implementing the CRFR is a multi-stage process that requires both strategic oversight and operational execution.
1: Governance Setup
- Assign a Resilience Officer or equivalent role.
- Establish a Resilience Steering Committee reporting to the Board.
- Approve a Resilience Policy.
2: Service Identification & Mapping
- Identify Critical Business Services (CBS).
- Map dependencies including technology, personnel, third-party vendors, and physical sites.
3: Risk Assessment & Scenario Analysis
- Conduct operational risk assessments.
- Perform impact tolerance analysis for each critical service.
4: Capability Building
- Implement technical measures (backup systems, failover sites).
- Train and equip incident management teams.
Stage 5: Testing & Validation
- Run simulation exercises (cyber incident drills, data center outage scenarios).
- Document results and feed into improvement plans.
6: Continuous Monitoring
- Use metrics and key risk indicators (KRIs) to monitor resilience performance.
- Conduct regular internal audits.
Services Offered for CRFR Implementation
Professional service providers help regulated entities comply with CRFR through:
| Service | Purpose | Example Deliverables |
|---|---|---|
| Resilience Gap Assessment | Identify current maturity vs CRFR requirements. | Maturity heatmap, gap analysis report. |
| Critical Service Mapping | Identify and map key processes and dependencies. | Dependency matrix, criticality scoring. |
| Impact Tolerance Setting | Define maximum acceptable downtime for services. | Tolerance thresholds, impact reports. |
| Resilience Architecture Design | Design IT and operational setups for high availability. | Architecture diagrams, failover plans. |
| Crisis Management Training | Equip leadership for decision-making in crises. | Workshop sessions, simulation results. |
| Third-Party Risk Review | Ensure vendors meet resilience standards. | Vendor resilience checklist, SLA enhancements. |
Checklist: Preparing for CRFR Compliance
Governance
- Board-approved resilience policy.
- Assigned Resilience Officer.
- Defined roles & responsibilities.
Critical Services
- List of critical services documented.
- Dependencies mapped (tech, people, vendors).
- Impact tolerance is defined.
Capabilities
- Backup and recovery systems are in place.
- Incident response team trained.
- Redundant systems tested.
Testing
- Crisis simulations are conducted quarterly.
- Lessons learned documented.
- Continuous improvement plan in progress.
Challenges in CRFR Adoption
- Complex Service Mapping – Financial services often have multiple interdependencies that are difficult to map completely.
- Vendor Compliance Gaps – Third parties may not meet required resilience standards.
- Cultural Shift – Moving from reactive to proactive resilience requires a mindset change.
- Resource Constraints – Budget and skilled staff availability.
- Data Management – Ensuring data integrity during disruptions.
Case Example (Hypothetical)
Institution: Najm Bank
Initial Status:
- Minimal formal resilience planning.
- Critical service dependencies are undocumented.
CRFR Implementation Steps:
- Conducted a resilience gap assessment (score: 48% compliant).
- Mapped 12 critical business services and their dependencies.
- Established a 2-hour maximum downtime threshold for key payment systems.
- Implemented redundant data center setup.
- Conducted quarterly cyber attack simulation drills.
Results:
- Achieved 95% compliance within 18 months.
- Reduced service recovery time by 60%.
- Enhanced regulator confidence.
Benefits of CRFR Compliance
- Operational Stability – Faster recovery from disruptions.
- Regulatory Trust – Positive audit outcomes.
- Customer Confidence – Maintaining service during crises.
- Financial Protection – Reduced losses from downtime.
- Market Reputation – Seen as a resilient, reliable institution.
Conclusion & Key Takeaways
The SAMA Cyber Resilience Framework for Regulated Entities is more than just another compliance checklist. It’s a blueprint for sustainable operational integrity in a world of increasing uncertainty.

