In an era where financial institutions are increasingly targeted by cyber threats, having a robust cybersecurity structure is no longer optional — it is a regulatory and operational necessity. Recognizing this, the Saudi Arabian Monetary Authority (SAMA), now the Saudi Central Bank, introduced its Cyber Security CSF framework to standardize and strengthen the cybersecurity posture across Saudi Arabia’s banking, insurance, and financial sectors.
While many organizations are now fully aligned with the CSF, the early implementation phase, from 2017 to 2019, was a transformative period. It set the groundwork for today’s mature compliance ecosystem. This article explores the background, objectives, early implementation process, services offered during the rollout, common challenges, and the long-term benefits of adopting the framework early.
What is the SAMA Cyber Security Framework (CSF)?
The SAMA CSF is a comprehensive set of cybersecurity requirements designed to help regulated entities:
- Protect sensitive data.
- Defend against cyber attacks.
- Ensure business continuity.
- Maintain trust with customers, regulators, and partners.
It aligns closely with international standards such as:
- ISO 27001 – Information Security Management Systems
- NIST Cybersecurity Framework
- PCI DSS – Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard
- CIS Controls
The framework provides a structured approach that covers governance, risk management, operations, and continuous improvement. Read more: Best Compliance Automation Tools
Background & Development of the SAMA CSF Framework
Why It Was Created
Before the CSF, cybersecurity practices among Saudi financial institutions were inconsistent. While some organizations had advanced security controls, others relied on minimal measures, leaving their critical infrastructure vulnerable.
Development Timeline
- 2016 – Initial drafts developed after consultations with local and international cybersecurity experts.
- May 2017 – Official release of the SAMA Cyber Security Framework.
- 2017–2019 – Early implementation phase; institutions were required to perform gap assessments and remediation plans.
- 2020 onwards – Updates introduced to address emerging threats like ransomware, cloud security risks, and supply chain vulnerabilities.
Core Objectives of the SAMA CSF
The framework has five main objectives:
| Objective | Description |
|---|---|
| Strengthen Cybersecurity | Improve resilience against cyber attacks across the financial sector. |
| Standardize Practices | Ensure a consistent cybersecurity baseline across all institutions. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Mandate minimum security measures to meet legal requirements. |
| Risk Mitigation | Identify, assess, and reduce cyber risks before they escalate. |
| Continuous Improvement | Create a culture of ongoing security monitoring and enhancement. |
Graphics Suggestion:
A five-segment infographic wheel representing the five objectives.
Early Implementation Phase (2017–2019)
The first wave of implementation was crucial. Institutions had to align their policies, procedures, and technologies with the CSF’s requirements — often from the ground up.
Key Activities in Early Implementation:
- Gap Assessment – Evaluating current cybersecurity maturity against CSF requirements.
- Roadmap Creation – Setting timelines and priorities for remediation.
- Policy & Process Development – Documenting governance and operational procedures.
- Control Implementation – Deploying security tools and technologies.
- Training & Awareness – Educating employees and executives.
- Readiness Audits – Internal and third-party audits before official inspections.
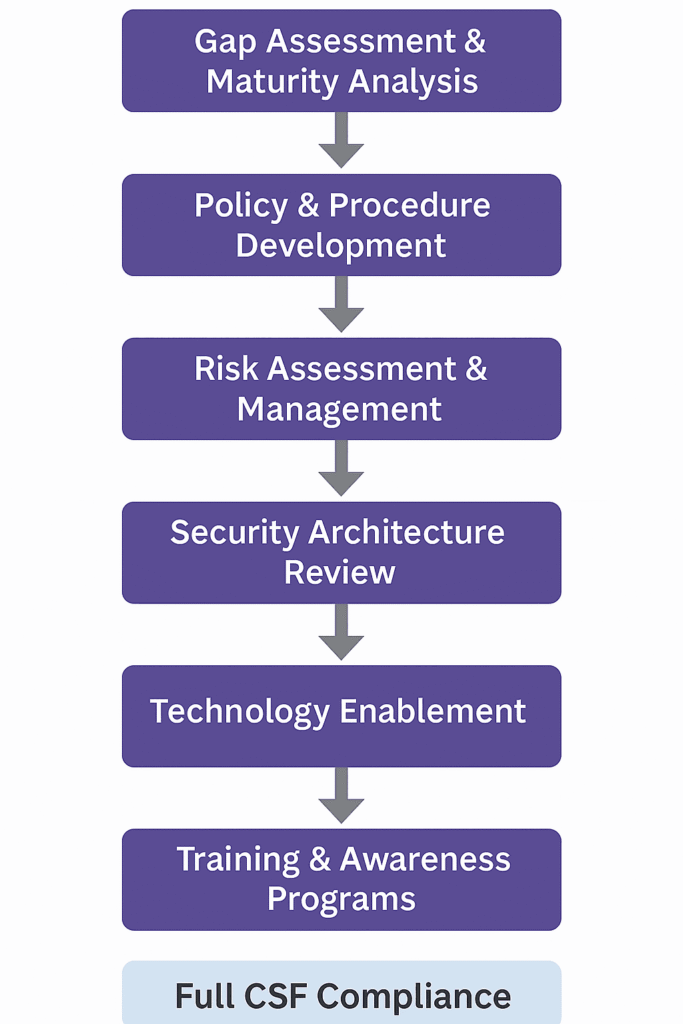
Services Provided for Early Implementation
During early rollout, several specialized services were offered by consultants, MSSPs, and compliance experts to help institutions comply effectively.
| Service | Purpose | Example Deliverables |
|---|---|---|
| Gap Assessment & Maturity Analysis | Identify where the current security posture falls short of CSF requirements. | Gap analysis report, maturity scorecards. |
| Policy & Procedure Development | Create governance and operational documents aligned with CSF domains. | Cybersecurity policy, incident response plan. |
| Risk Assessment & Management | Prioritize risks based on impact and likelihood. | Risk register, treatment plans. |
| Security Architecture Review | Ensure IT infrastructure supports CSF compliance. | Network diagrams, architecture improvement plan. |
| Technology Enablement | Deploy tools like SIEM, DLP, and IDS/IPS systems. | Tool configuration, integration documentation. |
| Training & Awareness Programs | Build a security-conscious culture. | Awareness sessions, phishing simulations. |
| Pre-Certification Audits | Prepare for regulator inspections. | Compliance checklist, audit readiness report. |
A service flowchart showing each service leading to “Full CSF Compliance” at the end.
Checklist: Preparing for SAMA CSF Compliance (Early Stage)
Governance & Leadership
- Board-approved cybersecurity strategy.
- Appointed Chief Information Security Officer (CISO).
- Defined roles and responsibilities.
Risk Management
- Conducted enterprise-wide risk assessment.
- Documented risk treatment plan.
- Regular review of emerging threats.
Operational Controls
- Incident response plan tested.
- Business continuity & disaster recovery plans in place.
- Regular vulnerability scanning & penetration testing.
Training & Awareness
- Security awareness training for all employees.
- Executive-level cybersecurity briefings.
- Social engineering simulations.
Monitoring & Improvement
- Implemented SIEM for real-time monitoring.
- Regular log reviews and threat hunting.
- Periodic framework compliance audits.
Common Challenges in Early Adoption
- Resistance to Change – Shifting from minimal security to full compliance required cultural change.
- Budget Constraints – Cybersecurity investment was often seen as a cost rather than a necessity.
- Talent Shortage – Limited availability of skilled cybersecurity professionals in the region.
- Legacy System Integration – Older systems lacked compatibility with modern security controls.
- Time Pressure – Regulatory deadlines left little room for gradual implementation.
Case Example (Hypothetical)
Institution: Al-Madina Bank
Scenario:
In 2017, Al-Madina Bank operated with basic firewalls and antivirus tools. After the CSF mandate:
- Conducted a gap assessment revealing 60% non-compliance.
- Developed a 12-month remediation plan.
- Hired a CISO and formed a cybersecurity committee.
- Implemented SIEM, DLP, and MFA solutions.
- Trained all employees on phishing awareness.
Outcome:
By early 2019, the bank achieved full CSF compliance and reduced security incidents by 45%.
Table: CSF Domains vs Services Offered
| CSF Domain | Typical Service Provided |
|---|---|
| Cybersecurity Governance | Policy drafting, governance framework setup |
| Risk Management | Risk assessments, treatment planning |
| Operations Management | Incident response playbooks, SOC setup |
| Third-Party Management | Vendor risk assessments |
| Cybersecurity Resilience | Business continuity planning |
| Compliance & Monitoring | Internal audits, readiness assessments |
Evolution After Early Rollout
After 2019, SAMA refined the CSF to address:
- Cloud Security – Adding controls for SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS environments.
- Ransomware Preparedness – Backup testing, incident playbooks.
- Supply Chain Security – Enhanced third-party risk assessments.
- OT Security – Addressing threats to operational technology systems.
Benefits of Early Adoption
- Regulatory Advantage – Passing inspections without last-minute panic.
- Enhanced Reputation – Market trust through compliance leadership.
- Operational Resilience – Reduced downtime from cyber incidents.
- Competitive Edge – Using compliance as a business differentiator.
- Cost Efficiency – Avoiding fines and incident recovery costs.
Conclusion & Key Takeaways
The early implementation of the SAMA Cyber Security Framework was more than a compliance exercise — it was a transformative moment for Saudi Arabia’s financial sector. Institutions that embraced it early not only met regulatory requirements but also built a lasting culture of cybersecurity resilience.